Theme of this issue
The theme of this issue is a sequel to the previous theme " Is it surprising that innovative medical devices don't require domestic clinical trials? Professional analysis→". The previous theme mainly summarized and analyzed the innovative device cases declared through non-domestic clinical trial data pathways in the review reports of CMDE, and we learned that there were 24 cases of innovative devices successfully registered through equivalent comparison clinical evaluation pathway. In this issue, a in-depth analysis chapter is specially launched with the intention of analyzing the successful cases of innovative devices underwent clinical evaluation through equivalent comparison and discussing the feasibility of reporting innovative devices through equivalent comparison.
Part I: Case analysis of equivalent comparison
In order to provide you with a deeper understanding of clinical evaluation through equivalent comparison pathway, we have specially selected one of the cases "3D Electronic Laparoscopy (CQZ2000577)" for in-depth analysis:
Product Introduction
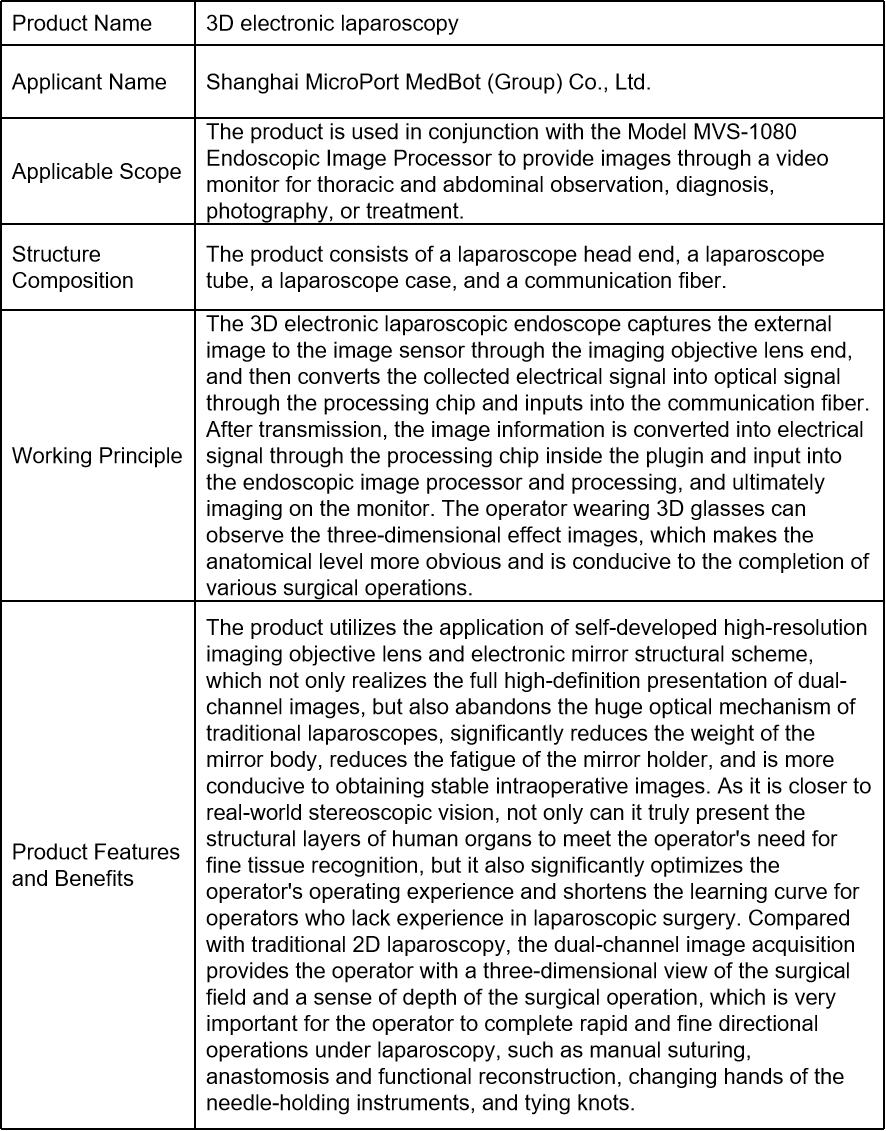
The product 3D electronic laparoscopy is the first domesticated 3D electronic laparoscope entering the green channel in China, and obtained the medical device registration certificate issued by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in June 2021, which broke the pattern of the international imported laparoscopy brand occupying the 3D laparoscopy market in China for a long time, and became one of the first commercialized 3D electronic laparoscopes developed by Chinese enterprises in China.
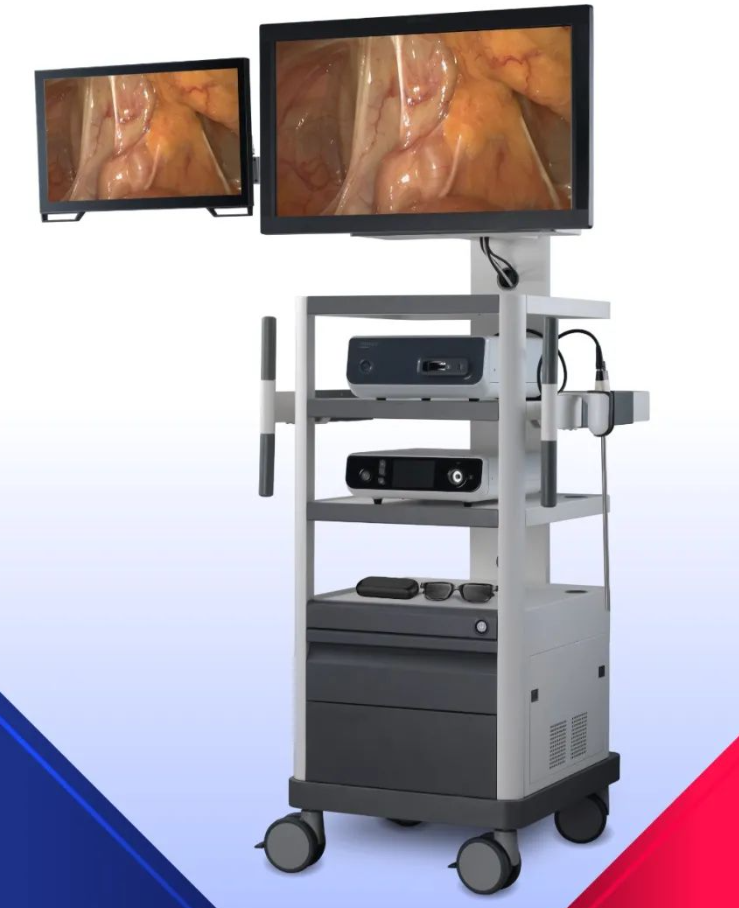 (Image from the official website of MicroPort MedBot)
(Image from the official website of MicroPort MedBot)
Product Classification
The management category of the product in this review report is class III.

Clinical Evaluation Pathway
The product in this review report selected the equivalent comparison for clinical evaluation.

Equivalent Comparison
The 3D electronic laparoscope and 3D high-definition electronic laparoscope (Registration Certificate No.: 20183222249 and 20163222452), which are already available on the market, were selected as the comparison products of the equivalent comparison.
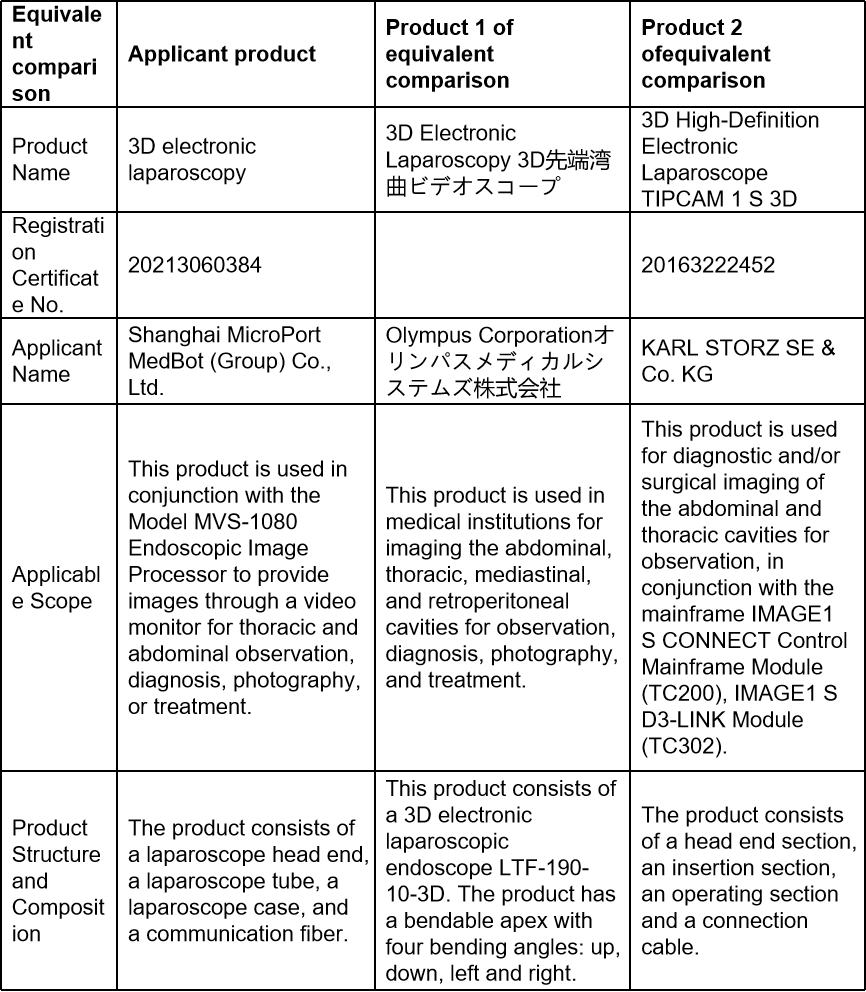

Overview of clinical evaluation
The applicant submitted a comprehensive comparison of the basic principle, structural composition, scope of application, etc., and provided test and comparison reports on performance parameters, etc., analysis reports on the safety and effectiveness of the difference parts, animal experiment data, clinical literature and clinical data of equivalent device to prove the safety and effectiveness of the applicant product.

Product Risk and Benefit Determination
Risk Analysis:
Benefits:
This product is a three-dimensional electronic laparoscopic endoscope, which can provide observation imaging of the location of the human thoracic and abdominal cavities. It can provide three-dimensional images for the surgeon during surgery, and provide a sense of longitudinal depth for intra-operative operations, so that the operations of tissue grasping, dissecting, separating, hemostasis, suturing and anastomosis can be easily realized.
Risks:
Improper handling of the endoscope may cause mechanical damage to human tissue; physicians with 3D vertigo may experience visual fatigue or dizziness during the procedure.

Part II: Summary
Through the above case analysis, we believe that you have a more in-depth understanding of the clinical evaluation of equivalent comparison, the core points are summarized below:
1. Selection of Clinical Evaluation Pathway: Accurately categorize the products according to their characteristics and select the appropriate clinical evaluation pathway by combining with the latest review requirements.
2. Selection of Comparator: One or more comparator products can be selected. If the applicant product combines design features or scope of application from multiple comparator devices, it is recommended that the registration applicant selects the product that is most similar to the applicant product as the main comparator device and minimizes the number of comparator devices.
3. Reference to Guidelines: Product-related registration review or clinical evaluation guidelines specify the key points of product registration review, and should be referred to when conducting clinical evaluation to ensure the accuracy and compliance of clinical evaluation.
4. Use of Non-clinical Evidence: The demonstration of safety and efficacy for innovations and other differences of innovative devices do not have to rely on clinical evidence, and only non-clinical evidence may be provided if non-clinical evidence is sufficient.
In the future, we will continue to provide innovative and high-risk medical devices clinical evaluation strategies and experiences sharing. Welcome everyone to stay tuned to our subsequent sharing of experiences! If you have any questions, please feel free to leave a message to communicate with us. See you in the next issue!
LINKS CRO
As a CRO company providing clinical trial services. LINKS CRO focus on innovation, high-risk implantation(intervention) medical device, with one-stop clinical trial solutions for the whole process of medical device research and development.The headquarters of LINKS is based in Shanghai, with subsidiary branches in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, in addition to ten regional offices. The current workforce comprises almost 200 employees, with technical personnel making up over 85% and dispersed across almost 30 cities nationwide. Key Services include CRO, SMO, CER, Audit, Post-market research, core laboratory registration both domestically and overseas, innovation declaration, Expert Consultancy, and overseas enterprise agency services. Key Indications include Cardiovascular, Neurovascular, Peripheral Vascular, Surgery Robot, Oncology, Ophthalmology, Medical Cosmetology, and other fields such as orthopedics. There are almost 300 projects consultations and services by LINKS each year.
