A detailed summary of CMDE public review reports were listed in the previous article ‘Is it surprising that innovative medical devices don't require domestic clinical trials? Professional analysis’. It was found that there were three paths for innovative medical devices to be registered through non-domestic clinical trial data, including equivalent comparison path, equivalent comparison combines with clinical trial data, and overseas clinical trial data. A total of 11 medical devices were identified that underwent clinical evaluation through a combination of equivalence comparison and clinical trial data.
How to efficiently conduct pre-market clinical evaluation of medical devices? The ‘Overview of Clinical Evaluation’ of public review reports of CMDE showed detailed description, but the situation wasn’t the same, which echoes with the response of the National Bureau of external consultation that ‘Applicants can submit registration information according to the actual situation of their own products.’ Upon a thorough review and analysis of the public review reports for the aforementioned 11 medical devices, it was observed that the clinical trial data could be categorized into two types, respectively, non-GCP and GCP clinical trial data. The former has not formed a universal standard yet, so it is difficult to accurately judge when submitting clinical trial data, on the contrary, the latter with clear guidelines issued by National Bureau clarified the submitting requirements, e.g. The Regulation and Quality Management of Clinical Trial of Medical Devices.
The following case study of clinical evaluation of Patient Monitor (CQZ2000927) is going to be analyzed.
Product Classification
According to the Classification Catalog of Medical Devices, it is a Class III medical device, the classification subcategory is 'Medical Diagnostic and Monitoring Devices (07)', the 1th category is 'Monitoring Devices (04)', the 2nd category is 'Patient Monitoring Devices (01)', and the classification code is 07-04-01.
Clinical Evaluation Pathway
The CMDE recommendation clinical evaluation is equivalent comparison path, while the actual was equivalent comparison combines with clinical trial.
Products Information
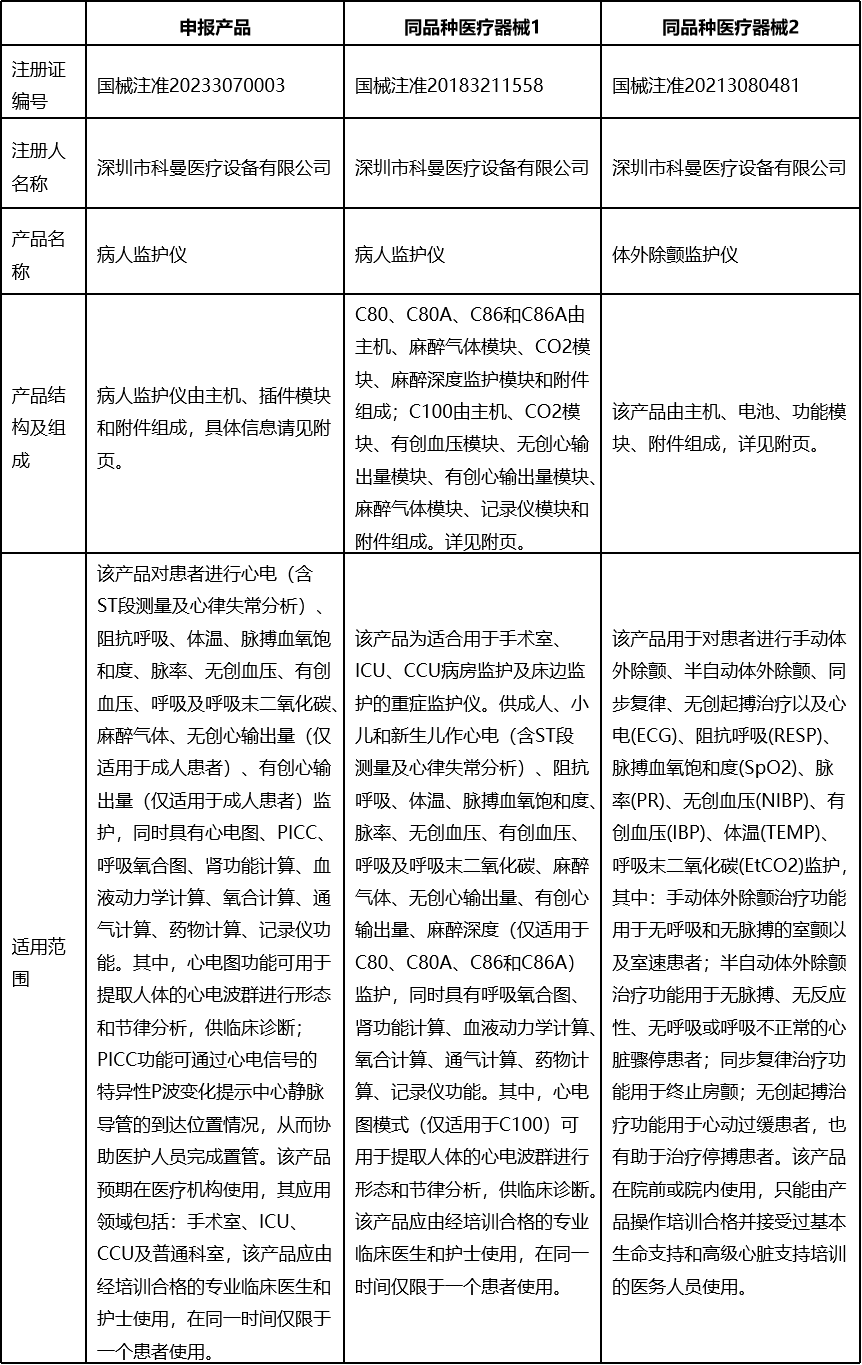
Equivalent-Comparison's Differences and Supporting Evidences
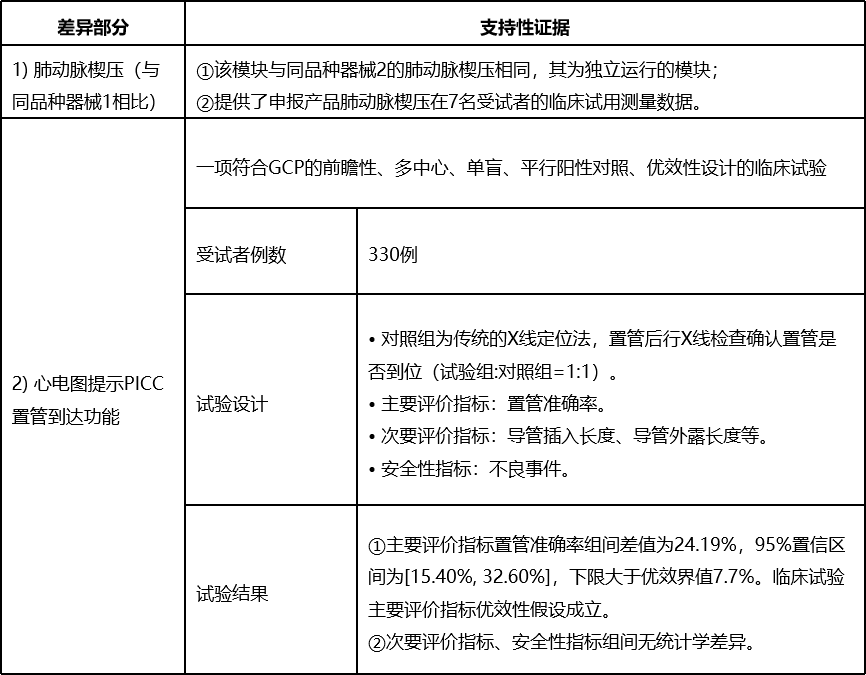
Product's Benefits and Risks
BENEFITS: This product monitors the patient's ECG (including ST-segment measurement and arrhythmia analysis), impedance respiration, temperature, pulse oximetry, pulse rate, noninvasive blood pressure, invasive blood pressure, respiratory and end-expiratory carbon dioxide, anesthesia gases, noninvasive cardiac output (only for adult patients), invasive cardiac output (only for adult patients), Additionally, it features functions such as ECG, PICC, respiratory oxygenation chart, renal function calculation, hemodynamic calculation, oxygenation calculation, ventilation calculation, drug calculation, recorder function. Among them, the ECG function can be used to show the human body's ECG wave groups for morphology and rhythm analysis for clinical diagnosis; the PICC function can indicate the placement of the central venous catheter through the specific P-wave change of the ECG signal, so as to assist the medical personnel in completing the placement of the catheter. The product is intended for use in medical institutions, and its application areas include: operating rooms, ICUs, CCUs and general departments. The product should be used by trained and qualified professional clinicians and nurses, and is limited to one patient at a time.
RISKS: In addition to the routine risks of patient monitor, the function indicating the presence of a central venous cannula in place by specific P-wave changes in the ECG signal may result in the physician re-catheterizing the cannula and delaying the consultation if there is an incorrect indication. Other risks may include:
1) Localized hematoma and subcutaneous bruising at the puncture site;
2) Damage to surrounding tissues such as nerves or lymphatic vessels;
3) Arrhythmia, cardiac arrest;
4) Leakage current risk;
5) Risk of infection from aseptic manipulation.
After a comprehensive evaluation, the benefits from the launch of this product are considered to outweigh the risks at the current level of awareness, and the combined residual risk is acceptable.
Summary
1. Is it always feasible to provide only non-clinical information when conducting clinical evaluations of equivalent comparison pathways? The answer is obviously no.
How to provide supporting information for the differences of the clinical evaluations of equivalent comparison pathways? In principle, providing sufficient evidences of the safety and effectiveness of the differences: 1) If the non-clinical data can demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the differences, then only non-clinical data is required; 2) If the non-clinical data is insufficient, then need to be supplemented with clinical trial data.
In this case study, for the PAWP difference between subject product and equivalent device, the comparable device with standalone PAWP function was added in the clinical evaluation; for the new function of subject product, PICC placement function indicated by ECG, because of higher risk, a GCP clinical trial was conducted to verify safety and effectiveness of the subject product.
2. Should the equivalent comparison pathway be abandoned when GCP clinical trial data is required as supporting evidence for the differences in the clinical evaluation of equivalent device. The answer is obviously no.
In this case study, the GCP clinical trial data submitted only for the declaration of the differences to verify the safety and effectiveness of subject product, it could greatly reduce the burden on applicants.
LINKS CRO
As a CRO company providing clinical trial services. LINKS CRO focus on innovation, high-risk implantation(intervention) medical device, with one-stop clinical trial solutions for the whole process of medical device research and development.The headquarters of LINKS is based in Shanghai, with subsidiary branches in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, in addition to ten regional offices. The current workforce comprises almost 200 employees, with technical personnel making up over 85% and dispersed across almost 30 cities nationwide.
Key Services include CRO, SMO, CER, Audit, Post-market research, core laboratory registration both domestically and overseas, innovation declaration, Expert Consultancy, and overseas enterprise agency services.
Key Indications include Cardiovascular, Neurovascular, Peripheral Vascular, Surgery Robot, Oncology, Ophthalmology, Medical Cosmetology, and other fields such as orthopedics. There are almost 300 projects consultations and services by LINKS each year.
